In 1936during excavations on a hill in a village southeast of BaghdadIn Iraqthe workers of the Iraqi Railways Department They discovered an old tomb covered with a stone slab. For two months, the Department of Antiquities extracted a multitude of artifacts and pieces whose age is estimated at nearly 2,000 years.
Among the discoveries, they found very unique clay containers, vase-shaped and yellow in color, which contained inside a copper cylinderfixed with asphalt to the neck of the vases, and with an iron rod inside, the application of which they did not know.
In 1938he German archaeologist Wilhelm Königlaboratory manager Baghdad State Museum, analyzed these objects and carried out an experiment by introducing an electrolyte into one of them. After plugging in a lamp, it lit very dimly. The later official report described that these devices behaved exactly like a modern electric battery, which is why they began to be known as “Baghdad Batteries”.
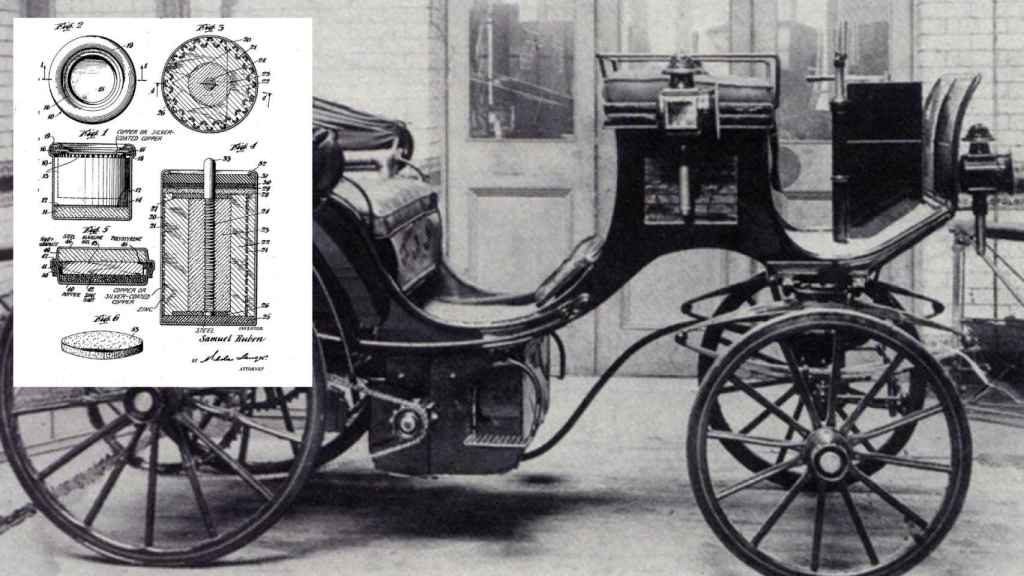
Ramón Gabarró’s electric car and patent for the first button cell.
Almost 20 centuries After the invention of these rudimentary batteries, a Spanish inventor created a revolutionary battery that was forgotten, until in the middle of the twentieth centuryan American used his work to create a new type of battery from which a legendary brand would be born that would change history: Duracell.
Ramón Gabarró and Julien He was a genius born in Manresa who had dedicated his life to making the world a better place through his inventions, leaving wonderful ideas for posterity.
He May 31, 1892 He obtained a patent for a new battery system compact, robust and cheap dry batteries that produced electrical energy and that made these batteries something never seen before, because having a powerful and reliable battery was not easy, in addition to the fact that they were the only ones marketed at that time They were used exclusively in workshops and laboratories.
But as usually happens, Ramon He was not a prophet in his country, therefore, in 1894he left to Paris Already London, where it tested its electrical system on some trams in these cities. Unfortunately for him, the political unrest of the time meant that his essays were not extremely popular, leading him to return to Spain without having succeeded in getting his ideas noticed by anyone.
[Francisco de Miranda, el independentista y traidor a España que fue perseguido por la Inquisición y murió en una cárcel de Cádiz]
The first Spanish electric vehicle
Taking advantage of the technology he had invented, 1896 decided to develop, for the queen Marie-Christine of Habsburg and Lorraineconsidered by many historians to be the first Spanish electric vehicle, based on a car chassis and elegant body made in London under his orders.

Marie-Christine of Habsburg and Lorraine.
Wikimedia Commons
with a little electric motorhave batteries less than 100 kilos and electric headlightsthis cart could reach 16 kilometers per hour and had an autonomy of 60 kilometers. Testing of the manufactured unit was carried out in London It was attended by the Spanish Ambassador, representatives of the Prince of Wales and major London newspapers. Ramón’s idea was to move the car to Madrid days after the tests, but It’s unclear what ultimately happened to this new vehicle.
[Juan de Salcedo, el Leónidas de Manila: defendió la isla de 3.000 piratas chinos con un escuadrón de 200 soldados españoles]
Email pioneer
During this year 1900, Ramon had another idea which can be considered a precursor to current email. Its goal was to distribute correspondence using electricity to make it faster than telegraph transmission. He started testing the year 1900 in the Madrid district of Prosperity and for this he designed a polygonal capsule, with the capacity to 1,000 cardswhich was powered by the railway’s power lines to reach high speeds.
He later carried out further tests using the power lines between Madrid And Aranjuezwith undeniable success, but he could not obtain the permits to continue his work, so his technology was relegated and forgotten, except for one Italian, Piscipelli Laeggiwho copied his idea and managed, a few years later, to get the government of his country to finance the installation, among Naples And Romeof the invention of Catalan.
Despite the success of all his tests, both his batteries and his mail transmission system, his ideas were forgotten. Ramón was ahead of his time, a pioneer, a precursor too bold and daring for the times in which he lived, which is why other geniuses used his work, but long after, he was no longer there. One of them was called Samuel Rubén.
[El mayor traidor español de todos los tiempos fue Antonio Pérez del Hierro: ayudó a crear la Leyenda negra y manipuló a Felipe II]
The button battery
In 1920business man Philip Rogers Mallory and the ingenious scientist Samuel Ruben They met by chance. Samuel needed a machine that Philip made in his company, Company Mallory PR, but when the two of them met, they decided to join forces. One would put inventive talent and the other entrepreneurial talent.
The company started its journey by manufacturing standard cells and batteries until the arrival of Second World Warwhen the U.S. government asked manufacturers for a product that could power the military’s communications equipment, flashlights, and mine detectors.

Mallory brand battery.
Wikimedia Commons
Samuel and Philip They created, thanks to the patent of this Catalan genius, what is called mercury button cellsmaller, larger capacity and resistant to the harshest climates of theaters of war, such as the north of Africa and the south of Peaceful, which the zinc-carbons could not support. In his patent, Samuel Ruben named the battery and the patent Ramonas part of his own invention.
They made millions of mercury batteries during the war, their technology made them millionaires, and they founded a new company. “The Mallory Battery Company”. For years, they continued to improve batteries, making them more compact and more durable than ever, until one day everything changed for them (and for us).
In the decade of 1960, the legendary Kodak launched its new innovative camera on the market, the Instamatic, a camera with a built-in flash and requiring more powerful and smaller batteries. To do this, The Mallory Battery Company created AAA batteries, a creation that would change human history forever.
The birth of Duracell
The photographic industry catapulted the company, as its batteries were needed all over the world, but Kodak required them to license their design to their competitors to ensure its availability in the consumer market. In doing so, they decided to register their trademark, 1965with the name of Duracell. His reputation reached such an extreme that, four years later, he became the first battery to set foot on lunar soil as part of the Apollo 11 mission.

Battery manufactured by Mallory with the new Duracell brand.
Wikimedia Commons
And all this thanks to a Catalan genius nineteenth century who was ahead of his time and just wanted to make the world a better place.

